Indonesia Propane Market (2025-2031) Outlook | Companies, Growth, Revenue, Trends, Analysis, Value, Forecast, Share, Industry & Size
| Product Code: ETC088487 | Publication Date: Jul 2023 | Updated Date: Feb 2026 | Product Type: Report | |
| Publisher: 6Wresearch | Author: Ravi Bhandari | No. of Pages: 70 | No. of Figures: 35 | No. of Tables: 5 |
Indonesia Propane Market: Import Trend Analysis
Indonesia`s propane market witnessed an import trend with a growth rate of 4.25% from 2023 to 2024, contrasting with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of -2.82% from 2020 to 2024. This shift in momentum could be attributed to changing demand dynamics or market stabilization efforts.

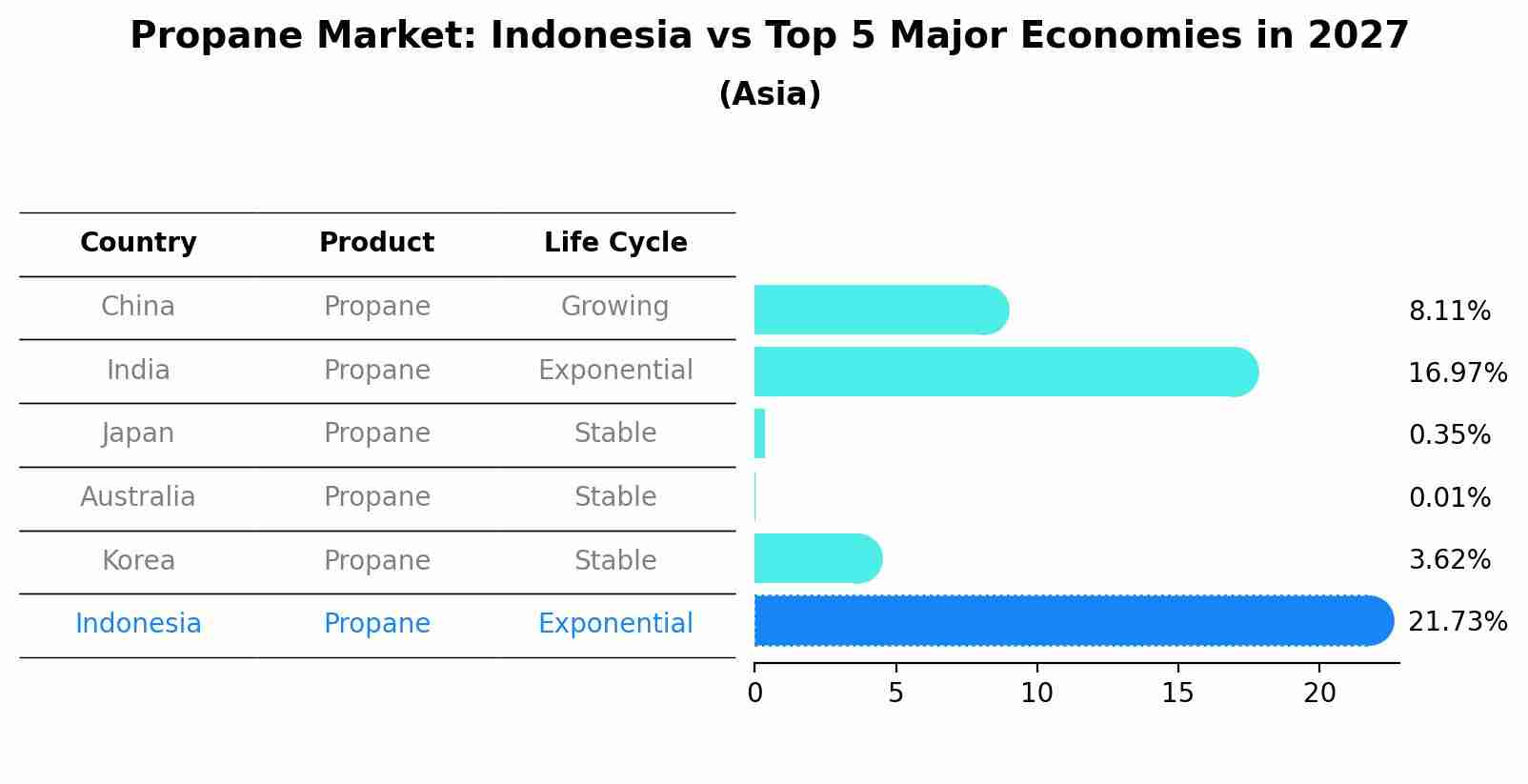
Propane Market: Indonesia vs Top 5 Major Economies in 2027 (Asia)
By 2027, the Propane market in Indonesia is anticipated to reach a growth rate of 21.73%, as part of an increasingly competitive Asia region, where China remains at the forefront, supported by India, Japan, Australia and South Korea, driving innovations and market adoption across sectors.
Indonesia Propane MarketSynopsis
Indonesia propane market is one of the fastest-growing markets in Southeast Asia. The market has seen a steady growth rate over the last few years, and this trend is likely to continue in the near future. The growing demand for clean energy sources, especially from industrial sectors, has been driving the Indonesia propane market for some time now. In addition, government initiatives such as tax incentives and subsidies have encouraged investments in alternative fuels like propane.
Market Trends
The trends observed in Indonesia propane industry include rising demand from residential consumers as well as an increased focus on safety measures due to stringent regulations enforced by local authorities. Additionally, there has been a rise in investment towards developing infrastructure related to storage and distribution networks of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). This development can be attributed to increased awareness among both producers and end users about its benefits compared to other forms of fuel such as kerosene or diesel.
Market Drivers
The primary drivers behind Indonesia increasing demand for LPG are population growth and urbanization along with significant campaigns undertaken by the government that promote LPG usage within households rather than traditional cooking methods like wood burning stoves which release large amounts of smoke into the atmosphere contributing negatively towards air pollution levels across cities & towns throughout Indonesia. Other factors that contribute significantly towards this sector are subsidized prices set up by state-run oil companies encouraging greater penetration even amongst lower income households while also providing efficient delivery systems across major towns & villages located throughout country island spread geography adding further impetus for adoption amongst people living in rural regions where access to power grids may not be available or reliable at all times.
COVID-19 Impact on the Market
In light of recent developments concerning COVID-19 pandemic, Indonesia Propane industry was slightly affected due to restrictions imposed on transportation which hampered deliveries while reduced availability caused temporary disruption during March & April months although majority operations returned back normalcy post relaxation period post May 2025. Consumers adapted themselves very quickly though adopting online ordering options provided large scale distributors through apps ensuring continuation needs could still be met without risk exposure.
Challenges of the Market
Despite tremendous efforts put forward by Government, Regional Authorities & Industry Stakeholders alike ; challenges remain including lack of proper infrastructure related issues resulting low accessibility areas impeding supply chain processes thus leading high costs associated with logistics. Furthermore difficulties arise when regarding regulatory framework since implementation procedures differ depending upon region causing compliance complexities difficulting overall business execution process throughout.
Industry Key Players
Pertamina, Energy Logistics Indonesia, PT Lintas Raya Utama, PT Sarana Gas Cemerlang, Indoguna Group, PT Mitra Usaha Mandiri Niaga (MUMN), Enviroenergi Prima Sejahtera, The Linde Group, Subur Jaya Energi Nusantara (SJEN), PT Cahaya Abadi Gasindo.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Indonesia Propane Market Outlook
- Market Size of Indonesia Propane Market, 2024
- Forecast of Indonesia Propane Market, 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Indonesia Propane Revenues & Volume for the Period 2021-2031
- Indonesia Propane Market Trend Evolution
- Indonesia Propane Market Drivers and Challenges
- Indonesia Propane Price Trends
- Indonesia Propane Porter's Five Forces
- Indonesia Propane Industry Life Cycle
- Historical Data and Forecast of Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume By Applications for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume By Industrial for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume By Commercial for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume By Residential for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume By Transportation for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume By Agriculture for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume By Chemicals and Refineries for the Period 2021-2031
- Indonesia Propane Import Export Trade Statistics
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Applications
- Indonesia Propane Top Companies Market Share
- Indonesia Propane Competitive Benchmarking By Technical and Operational Parameters
- Indonesia Propane Company Profiles
- Indonesia Propane Key Strategic Recommendations
Frequently Asked Questions About the Market Study (FAQs):
1 Executive Summary |
2 Introduction |
2.1 Key Highlights of the Report |
2.2 Report Description |
2.3 Market Scope & Segmentation |
2.4 Research Methodology |
2.5 Assumptions |
3 Indonesia Propane Market Overview |
3.1 Indonesia Country Macro Economic Indicators |
3.2 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume, 2021 & 2031F |
3.3 Indonesia Propane Market - Industry Life Cycle |
3.4 Indonesia Propane Market - Porter's Five Forces |
3.5 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Applications, 2021 & 2031F |
4 Indonesia Propane Market Dynamics |
4.1 Impact Analysis |
4.2 Market Drivers |
4.2.1 Growing industrial applications of propane in Indonesia |
4.2.2 Increasing adoption of propane as a cleaner alternative fuel |
4.2.3 Government initiatives promoting the use of propane for cooking and transportation |
4.3 Market Restraints |
4.3.1 Lack of infrastructure for propane distribution and storage |
4.3.2 Fluctuating propane prices in the global market affecting Indonesia's market |
4.3.3 Competition from alternative energy sources like natural gas and electricity |
5 Indonesia Propane Market Trends |
6 Indonesia Propane Market, By Types |
6.1 Indonesia Propane Market, By Applications |
6.1.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.1.2 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume, By Applications, 2021-2031F |
6.1.3 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume, By Industrial, 2021-2031F |
6.1.4 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume, By Commercial, 2021-2031F |
6.1.5 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume, By Residential, 2021-2031F |
6.1.6 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume, By Transportation, 2021-2031F |
6.1.7 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume, By Agriculture, 2021-2031F |
6.1.8 Indonesia Propane Market Revenues & Volume, By Chemicals and Refineries, 2021-2031F |
7 Indonesia Propane Market Import-Export Trade Statistics |
7.1 Indonesia Propane Market Export to Major Countries |
7.2 Indonesia Propane Market Imports from Major Countries |
8 Indonesia Propane Market Key Performance Indicators |
8.1 Number of new industrial applications adopting propane in Indonesia |
8.2 Percentage increase in propane consumption for cooking and transportation |
8.3 Investment in infrastructure development for propane distribution and storage in Indonesia |
9 Indonesia Propane Market - Opportunity Assessment |
9.1 Indonesia Propane Market Opportunity Assessment, By Applications, 2021 & 2031F |
10 Indonesia Propane Market - Competitive Landscape |
10.1 Indonesia Propane Market Revenue Share, By Companies, 2024 |
10.2 Indonesia Propane Market Competitive Benchmarking, By Operating and Technical Parameters |
11 Company Profiles |
12 Recommendations |
13 Disclaimer |
Export potential assessment - trade Analytics for 2030
Export potential enables firms to identify high-growth global markets with greater confidence by combining advanced trade intelligence with a structured quantitative methodology. The framework analyzes emerging demand trends and country-level import patterns while integrating macroeconomic and trade datasets such as GDP and population forecasts, bilateral import–export flows, tariff structures, elasticity differentials between developed and developing economies, geographic distance, and import demand projections. Using weighted trade values from 2020–2024 as the base period to project country-to-country export potential for 2030, these inputs are operationalized through calculated drivers such as gravity model parameters, tariff impact factors, and projected GDP per-capita growth. Through an analysis of hidden potentials, demand hotspots, and market conditions that are most favorable to success, this method enables firms to focus on target countries, maximize returns, and global expansion with data, backed by accuracy.
By factoring in the projected importer demand gap that is currently unmet and could be potential opportunity, it identifies the potential for the Exporter (Country) among 190 countries, against the general trade analysis, which identifies the biggest importer or exporter.
To discover high-growth global markets and optimize your business strategy:
Click Here- Single User License$ 1,995
- Department License$ 2,400
- Site License$ 3,120
- Global License$ 3,795
Search
Thought Leadership and Analyst Meet
Our Clients
Related Reports
- Pakistan Contraceptive Implants Market (2025-2031) | Demand, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Companies, Challenges
- Sri Lanka Packaging Market (2026-2032) | Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges, Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints
- India Kids Watches Market (2026-2032) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Saudi Arabia Core Assurance Service Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Romania Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Market (2026-2032) | Industry, Analysis, Revenue, Size, Forecast, Outlook, Value, Trends, Share, Growth & Companies
- Saudi Arabia Car Window Tinting Film, Paint Protection Film (PPF), and Ceramic Coating Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- South Africa Stationery Market (2025-2031) | Share, Size, Industry, Value, Growth, Revenue, Analysis, Trends, Segmentation & Outlook
- Afghanistan Rocking Chairs And Adirondack Chairs Market (2026-2032) | Size & Revenue, Competitive Landscape, Share, Segmentation, Industry, Value, Outlook, Analysis, Trends, Growth, Forecast, Companies
- Afghanistan Apparel Market (2026-2032) | Growth, Outlook, Industry, Segmentation, Forecast, Size, Companies, Trends, Value, Share, Analysis & Revenue
- Canada Oil and Gas Market (2026-2032) | Share, Segmentation, Value, Industry, Trends, Forecast, Analysis, Size & Revenue, Growth, Competitive Landscape, Outlook, Companies
Industry Events and Analyst Meet
Whitepaper
- Middle East & Africa Commercial Security Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East & Africa Fire Safety Systems & Equipment Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Drone Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East Lighting Fixture Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Physical & Perimeter Security Market Click here to view more.
6WResearch In News
- Doha a strategic location for EV manufacturing hub: IPA Qatar
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Empowering Growth: The Thriving Journey of Bangladesh’s Cable Industry
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Video call with a traditional healer? Once unthinkable, it’s now common in South Africa
- Intelligent Buildings To Smooth GCC’s Path To Net Zero


















